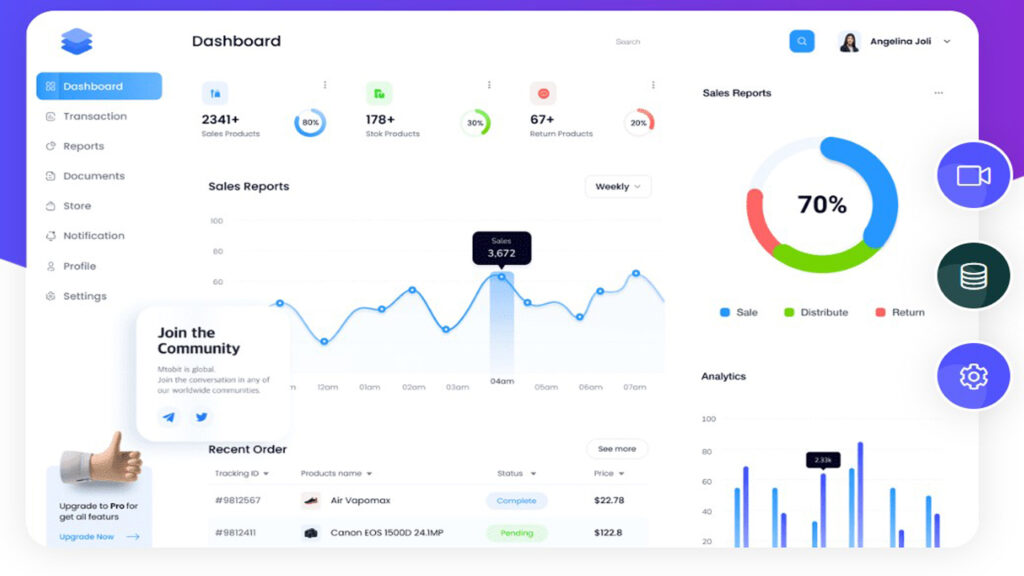
Introduction and overview of SaaS (Software-as-a-Service) analytics
In the SaaS world, analytics mean collecting and reporting on data streams received from SaaS applications such as a CRM, marketing automation, ERP and others. As more companies are implementing SaaS solutions and storing data in the cloud, they are in need of ways to understand all this data and get business insights.
Some key things to know about SaaS analytics:
- It provides a single platform for them to analyze the data generated from various SaaS applications instead of using various analytical tools or resorts separately. Here the goal is not only to present but to provide a unified view.
- Typical use cases include studying the patterns of customers’ preferences and behavior received from CRM systems, the marketing campaign indicators from marketing tools, the financial flow patterns from ERP tools and many others.
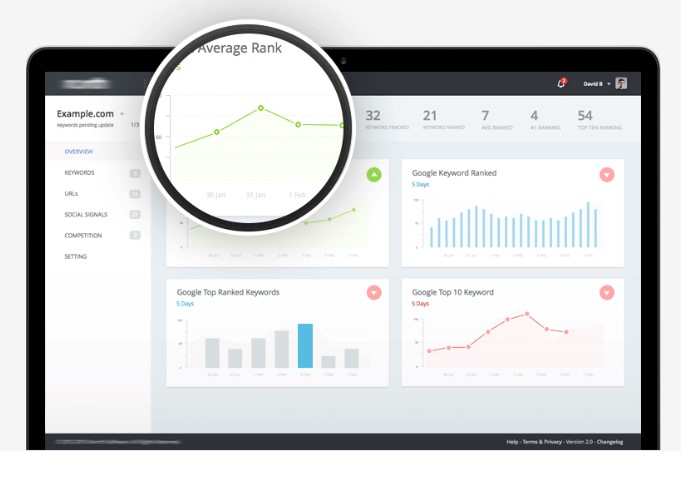
- It can make visible the insights that would be barely visible had the data been seen separately rather than as an entire source of inscriptions. Patterns and correlations arise from consolidated data but the way they are reflected is another story.
- The specially developed SaaS analytics tools and integrations have come into play to handle the complex data structures, metadata, and access rules for factious SaaS systems in order to unify the analytics environments.
- The advantages include integration across apps, no data silos, using AI-enabled analytics, tracking of KPIs, finding trends and abnormalities, process enhancement, issue identification, and proactive solutions.
SaaS analytics differs from other forms of analytics in providing the companies with a holistic data analysis from multiple cloud apps to make informed and data-driven business decisions. This scenario has come about due to rising number of enterprise SaaS adoption. Hence, analytics platform that support this ecosystem are as vital as the SaaS itself.
How SaaS analytics helps to improve business economics
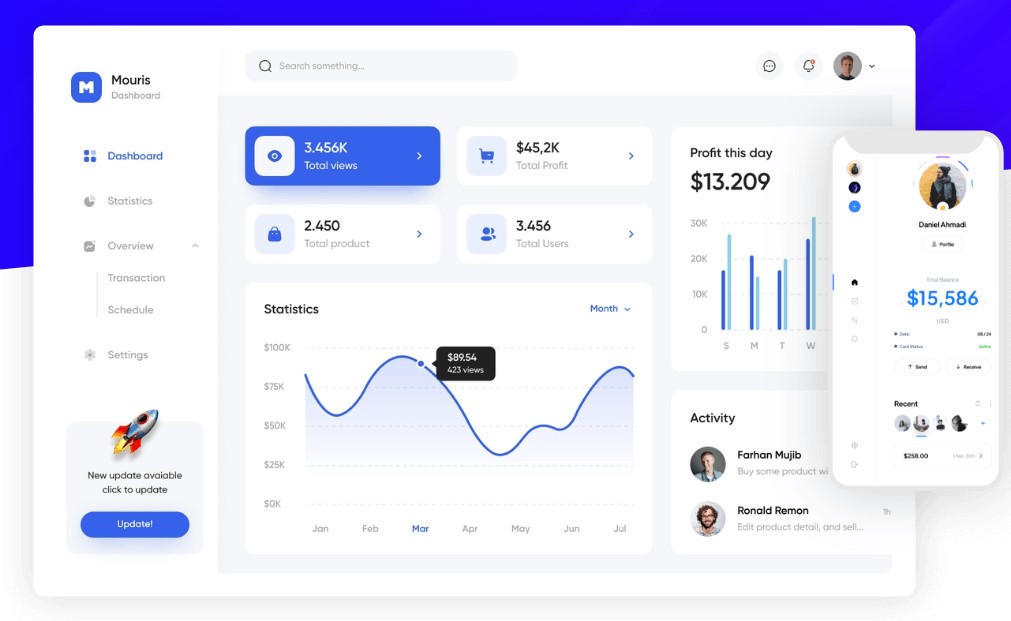
SaaS analytics can help improve business economics in a few key ways:-
1. Better data-driven decisions:- SaaS companies can use data analysis to conclude a result of usage patterns, customer behavior, sales funnels, etc. which in turn makes it possible to make smart decisions regarding product, pricing and go-to-market strategies. This is actually what creates higher conversion rates, churn, and allows for better optimization practices.
2. Increased operational efficiency:- SaaS analytics offers a glimpse of resource usage, infrastructure expenditure, support ticket analysis, and so on. This in turn fuels companies to streamline processes, minimize wastage and improve effectiveness, thus lowering their expenses at the same time.
3. Pricing optimization:- The analytics allow companies to get the insight into consumers readiness to pay, features of the product, user profiles and other attributes to develop the most appropriate pricing plans and package up the products. Hence, will enable the maximum revenue with optimum customer satisfaction.

4. Customer segmentation:- The businesses may follow the practice of gathering customers under the same roof by the application of the common attributes from the analytics data. In turn, these businesses can design product offerings and ads which target each segment, leading to higher uptake and engagement.
5. Expansion revenue:- Usage and adoption data will always make a company to get insights into when and where the upsell and cross-sell prospective customers can be identified to drive expansion revenue from these same customers, which in turn improves the business economics.
In the nutshell, data and analytics are the crucial components intended to company either by gaining user efficiency, maximizing customer lifetime value, operating leaner, or by making wiser decisions so that it can achieve better performance over time.
Importance of Analytics in Business Economics
Analytics play a critical role in business economics in several ways:–
- Demand forecasting:- Analysis of previous sales data, economic trends, demographics, and other data creates more real forecasts. This offers them opportunity to define the supply plans, budgets for inventory, marketing as well as other expenditures in a more precise way.
- Pricing optimization:- Sales elasticity, pricing, segments, customer (readiness-to-pay) participation should be taken into account by businesses if they would like to create a data-driven pricing model that maximizes their revenues. Another role of analytics in the booking and travel sector is that it has the ability to create clear, different prices for different clients depending on their travel type.
- Customer analysis:- This includes customer analytics that allows us to identify such a set of criteria as customer preferences, customer lifetime value, churn risks, the most promising profiles for acquisition, and the best customer experience investments to ensure loyalty and retention. This information helps us develop the better marketing strategy and customer strategy in general.

- Market basket analysis:- As soon as understanding what customers buy together is clear, placing complementary merchandise, promotions to attain the higher order values possible, laying out a store neatly, and customized recommendations become doable. This creates more shopping and brings in more money.
- Analytics reveals what production and remedial cost, manipulates an efficient logistics network and eliminates wastes and stockouts. As a result, the operation becomes the optimal one where invoices are put at bay, working capital is fully used, and high margin is achieved.
Basically, analytics makes business decisions less intuitive and more information based, which according to data and quantitative analysis improves productivity, profits and the business competitive edge. It depicts companies as data science-based instruments for the creation of value.
Key features and functionalities of SaaS analytics platforms
Here are some of the key features and functionalities commonly found in SaaS (Software-as-a-Service):-
- Being SaaS
- Vertical scalability
- Self-service analytics
- Pre-constructed reports, metrics, and dashboards
- Data integration
- Collaboration staples
- Personalization and expandability
- Mobility access
- Security features
Being SaaS
- The SaaS analytics platform provided by cloud service is hosted in the cloud, therefore allowing access from anywhere with internet connection without need of installing software locally.
Vertical scalability
- It scales easily upwards or downwards to process more data storage, user number, etc. as the demand grows. Scale becomes effortless due to the cloud-based character that makes it possible.
Self-service analytics
- They are the ones that allow managers and process specialists even across the whole organization to build reports, scour data, create visualizations and dashboards on their own without the assistance of IT support or analysts.
Also Read:- Enhancing Efficiency: How Small Business IT Support Services Can Transform Your Operations

Pre-constructed reports, metrics, and dashboards
- Almost all platforms have preconfigured reports, KPIs and dashboards in place that can be used for implementing common business tasks immediately. Users are able to modify their tracks as well.
Data integration
- They offer connectors used to import/export data from different sources i.e. databases, CRM systems, ERP systems and always be ready to analyze data from multiple sources.
Collaboration staples
- This can include sharing reports, findings, and annotations outside the Professionals under the same organization.
Personalization and expandability
- APIs and developer tools also supplied to extend the platform functionalities for business-specific purposes.
Mobility access
- Business users can log in on their smartphones and tablets to open mobile apps anytime, which allows them to access reports and analytics from anywhere.
Security features
- Role-based access control, data encryption and so on make company data secure and analytics protected.
The Role of SaaS Analytics in Business Economics
The analytics in SaaS help the organizations to be aware of the actions of the customers. Through the metrics they get to understand where to improve by tracking metrics like engagement, churn, and lifetime value. They also marketing to the customer needs.
With SaaS analytics, enterprises are able to measure user behavior, allocation of resources, and system efficiency in order to improve workflow as well as streamline it. Incoherence prevention may lead to a decrease in expenditures.
Together with the date and tendency visible for the business via SaaS analytics, it is easier for them to predict how the performance will be in the future. Correct forecasts make the future plannining and budgeting process more intelligent.
In-depth data analytics driven by Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) can be used by enterprises to develop market opportunities and also to create unique value propositions for customers that are an essential competitive advantage. There is a kind of economic effect that is derived from having access to data that competitors were not able to touch.
Essentially, SaaS analytics tools help business to gather facts that enable them to make decision based on what they see. Thus, the effects of enhanced productivity chain comprise cost reductions, increased earnings and better economic performance. These AI powered tools have proven to be one of a kind in the modern data driven business economics.
Key Metrics and KPIs in SaaS Analytics
Here are some of the key metrics and KPIs:
- Monthly Recurring Revenue (MRR)
- Annual recurring revenue (ARR)
- Churn rate
- Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC)
- Lifetime value (LTV)
- Activation rate:
- Net revenue retention
- Customer Lifetime
- Sales cycle span
- Monthly Active Users (MAU)
- The speed
Monthly Recurring Revenue (MRR)
- The sum of all revenue received monthly from subscriptions, plus any recurring services. A key growth metric.
Annual recurring revenue (ARR)
- Yearly income earned from all the subscriptions system and recurring services. Shows overall business value.
Churn rate
- The ratio of the customers who cancel subscriptions over a certain time to those who retain their subscriptions. Lower churn is better.
Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC)
- The cost to attain a new customer. Lower is better.
Lifetime value (LTV)
- The cumulated income from a customer throughout their lifespan. LTV (customer lifecycle value ) to CAC (customer acquisition cost) ratio measures ROI of marketing.
Activation rate
- The number of free trial users who change to paying members. Higher is better.
Net revenue retention
- Revenue retained from existing customers minus churn (churn rate = number of clients that are lost due to churn). Below 100% demonstrates growth from curtailment.
Customer Lifetime
- The average duration of time, in months or years, a customer will continue to be active. Longer is better.
Sales cycle span
- The duration of the process of bringing a new sale to completion. Shorter cycles improve efficiency.
Monthly Active Users (MAU)
- The number of Unique users who have been active in a Month. Shows engagement.
The speed
- The percentages of daily active users and monthly active users of a given app from the total users. Higher means more loyalty.
Monitoring these metrics after a certain period of time will allow benchmarking progress and finding out the areas of the highest priority that need to be given more attention to decrease churn, increase activation, or improve marketing processes. Whether an SaaS company is renting or selling its services and looking for a profit or market dominance depends on the KPIs it chooses to focus on.
Conclusion
In short, a data strategy that involves using analytics at all levels empowers SaaS companies to not only develop intelligent products and pricing strategies, but also to improve operations. Metrics and insights obtained from usage of analytics aid in the task of churn prevention, growing customer lifetime value, lowering acquisition cost, and monetizing the feature use to the fullest. Organizations which have sustainable competitive advantage through improved economics, are quantum leaps better than those which implement continuous trialing and optimization using analytics.